目标检测YOLOv3笔记(4):输入图片数据预处理
YOLOv3对图片进行检测前,先要对图片进行预处理,先进行转换再进行resize使其和网络输入大小一致。这个过程使用demo的cpu方法对于大图片会花费很多实际。1080P的图片大概需要100ms左右。
因此仔细研究这个预处理过程的代码,并将其转换为使用cuda在GPU里进行预处理相信可以快很多。
首先传入图片是使用opencv的mat类型,这里主要做了两个操作,如下图所示:
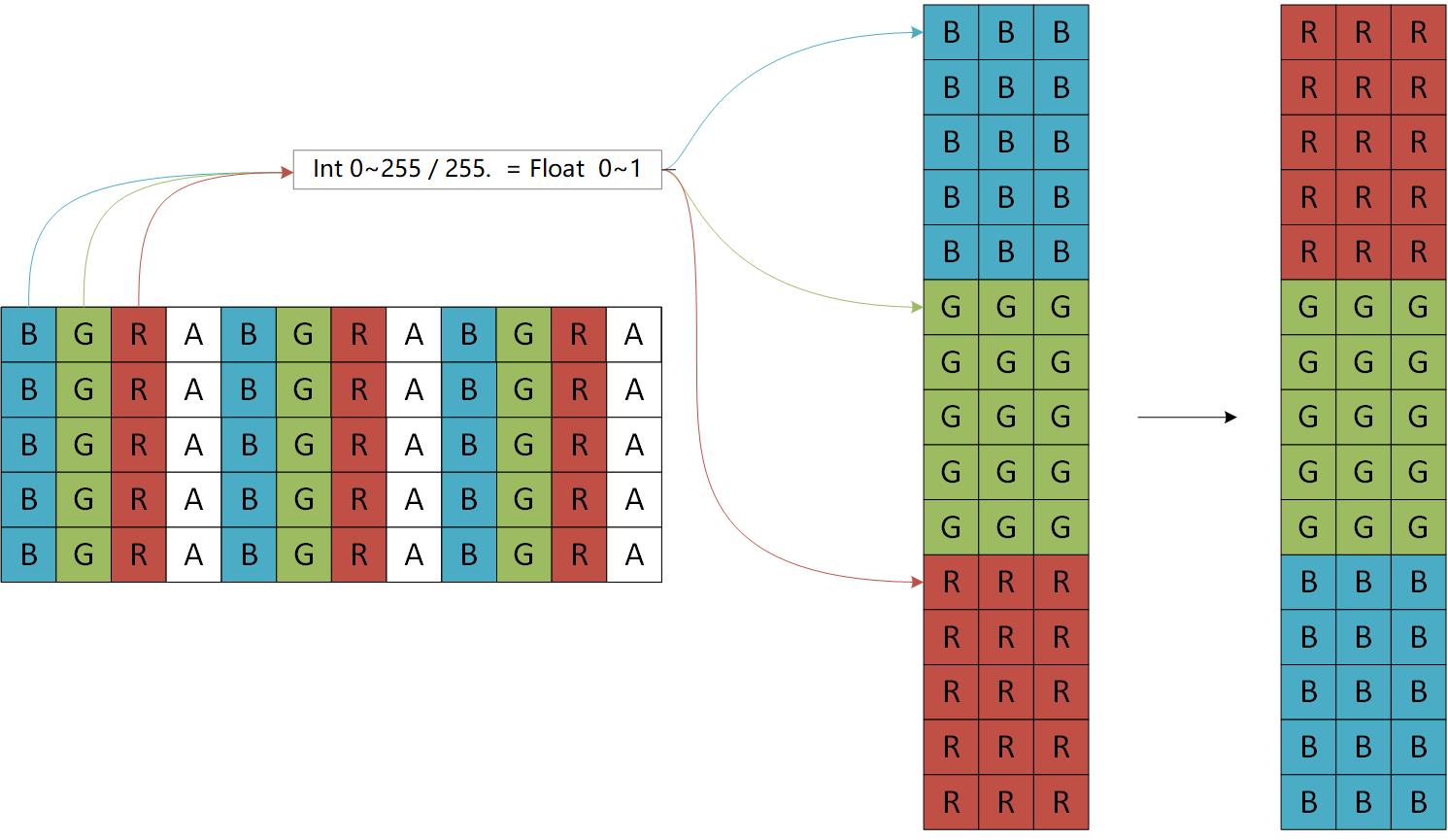
这个过程其实就是 ipl_to_image 转为0~1的浮点数并归集B通道G通道R通道 -> rgbgr_image 转换为 R通道G通道B通道的顺序
原代码:
image mat_to_image(Mat m)
{
IplImage ipl = m;
image im = ipl_to_image(&ipl);
rgbgr_image(im);
return im;
}
image ipl_to_image(IplImage* src)
{
int h = src->height;
int w = src->width;
int c = src->nChannels;
image im = make_image(w, h, c);
unsigned char *data = (unsigned char *)src->imageData;
int step = src->widthStep;
int i, j, k;
for(i = 0; i < h; ++i){
for(k= 0; k < c; ++k){
for(j = 0; j < w; ++j){
im.data[k*w*h + i*w + j] = float(data[i*step + j*c + k]/255.);
}
}
}
return im;
}这个用cuda的核函数很方便可以实现
void convert_to_yolo_image_kernel(const uint8_t* src, uint32_t srcPitch, float *dst , uint32_t width, uint32_t height)
{
const uint32_t x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const uint32_t y = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (x < width && y < height) {
const uint32_t sBGRA = y * srcPitch + 4 * x;
const uint32_t dR = y * width + x;
const uint32_t dG = width * height + y * width + x;
const uint32_t dB = 2 * width * height + y * width + x;
dst[dR] = (float) (src[sBGRA + 2] / 255.);
dst[dG] = (float) (src[sBGRA + 1] / 255.);
dst[dB] = (float) (src[sBGRA] / 255.);
}
}接下来是做了resize处理,reszie的时候是跟据原图的纵横比来决定等比例缩放的比例,以达到最大匹配网络输入大小,等比例缩放后再通过填充使其尺寸与网络输入尺寸一致,原代码如下:
image letterbox_image(image im, int w, int h)
{
int new_w = im.w;
int new_h = im.h;
if (((float)w/im.w) < ((float)h/im.h)) {
new_w = w;
new_h = (im.h * w)/im.w;
} else {
new_h = h;
new_w = (im.w * h)/im.h;
}
image resized = resize_image(im, new_w, new_h);
image boxed = make_image(w, h, im.c);
fill_image(boxed, .5);
embed_image(resized, boxed, (w-new_w)/2, (h-new_h)/2);
free_image(resized);
return boxed;
}image resize_image(image im, int w, int h)
{
image resized = make_image(w, h, im.c);
image part = make_image(w, im.h, im.c);
int r, c, k;
float w_scale = (float)(im.w - 1) / (w - 1);
float h_scale = (float)(im.h - 1) / (h - 1);
for(k = 0; k < im.c; ++k){
for(r = 0; r < im.h; ++r){
for(c = 0; c < w; ++c){
float val = 0;
if(c == w-1 || im.w == 1){
val = get_pixel(im, im.w-1, r, k);
} else {
float sx = c*w_scale;
int ix = (int) sx;
float dx = sx - ix;
val = (1 - dx) * get_pixel(im, ix, r, k) + dx * get_pixel(im, ix+1, r, k);
}
set_pixel(part, c, r, k, val);
}
}
}
for(k = 0; k < im.c; ++k){
for(r = 0; r < h; ++r){
float sy = r*h_scale;
int iy = (int) sy;
float dy = sy - iy;
for(c = 0; c < w; ++c){
float val = (1-dy) * get_pixel(part, c, iy, k);
set_pixel(resized, c, r, k, val);
}
if(r == h-1 || im.h == 1) continue;
for(c = 0; c < w; ++c){
float val = dy * get_pixel(part, c, iy+1, k);
add_pixel(resized, c, r, k, val);
}
}
}
free_image(part);
return resized;
}整理处理流程,如下图所示:
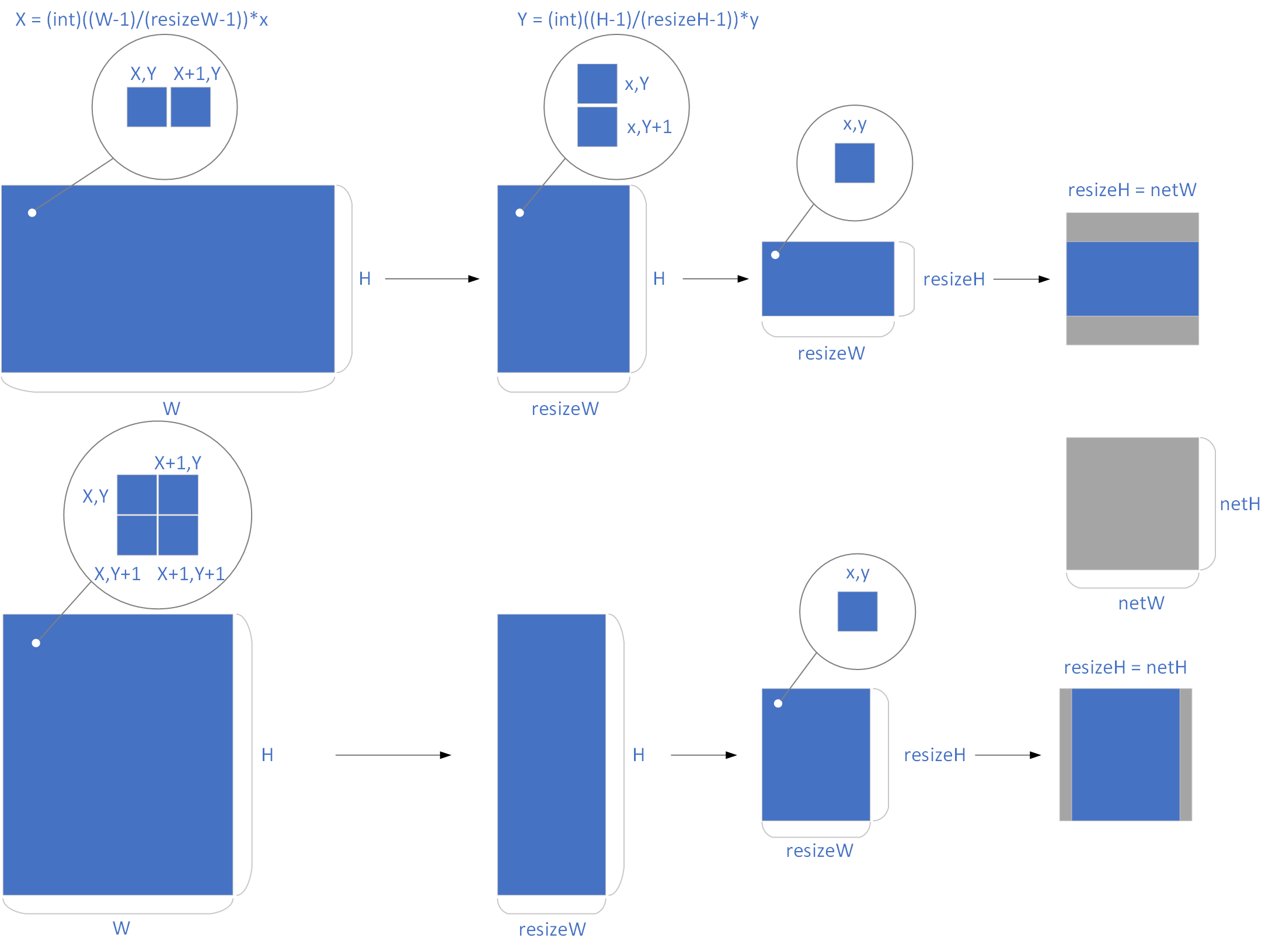
可以看出,这个缩放其实就是双线性插值法,缩放后图片其实就是原图相对坐标位置临近的四个点取插值。一开始我是用核函数按照原代码分步依次实现:
__global__
void part_yolo_image_kernel(const float* src, float *dst , uint32_t resizeW, uint32_t width, uint32_t height)
{
const uint32_t x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const uint32_t y = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (x < resizeW && y < height) {
const uint32_t dR = y * resizeW + x;
const uint32_t dG = resizeW * height + y * resizeW + x;
const uint32_t dB = 2 * resizeW * height + y * resizeW + x;
const uint32_t step = width * height;
if (x == resizeW - 1 || width == 1) {
dst[dR] = src[y * width + width - 1];
dst[dG] = src[width * height + y * width + width - 1];
dst[dB] = src[2 * width * height + y * width + width - 1];
} else {
float sx = x * (float) (width - 1) / (resizeW - 1);
int ix = (int) sx;
float dx = sx - ix;
dst[dR] = (1 - dx) * src[y * width + ix] + dx * src[y * width + ix + 1];
dst[dG] = (1 - dx) * src[step + y * width + ix] + dx * src[step + y * width + ix + 1];
dst[dB] = (1 - dx) * src[2 * step + y * width + ix] + dx * src[2 * step + y * width + ix + 1];
}
}
}__global__
void resize_yolo_image_kernel(const float* src, float *dst , uint32_t resizeW, uint32_t resizeH, uint32_t height) {
const uint32_t x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const uint32_t y = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (x < resizeW && y < resizeH) {
const uint32_t dR = y * resizeW + x;
const uint32_t dG = resizeW * resizeH + y * resizeW + x;
const uint32_t dB = 2 * resizeW * resizeH + y * resizeW + x;
const uint32_t step = resizeW * height;
float sy = y * (float) (height - 1) / (resizeH - 1);
int iy = (int) sy;
float dy = sy - iy;
if (y == resizeH - 1 || height == 1) {
dst[dR] = (1 - dy) * src[iy * resizeW + x];
dst[dG] = (1 - dy) * src[step + iy * resizeW + x];
dst[dB] = (1 - dy) * src[2 * step + iy * resizeW + x];
} else {
dst[dR] = (1 - dy) * src[iy * resizeW + x] + dy * src[(iy + 1) * resizeW + x];
dst[dG] = (1 - dy) * src[step + iy * resizeW + x] + dy * src[step + (iy + 1) * resizeW + x];
dst[dB] = (1 - dy) * src[2 * step + iy * resizeW + x] + dy * src[2 * step + (iy + 1) * resizeW + x];
}
}
}__global__
void embed_yolo_image_kernel(const float* src, float *dst , uint32_t resizeW, uint32_t resizeH, uint32_t netW, uint32_t netH) {
const uint32_t x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const uint32_t y = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
if (x < netW && y < netH) {
const uint32_t dR = y * netW + x;
const uint32_t dG = netW * netH + y * netW + x;
const uint32_t dB = 2 * netW * netH + y * netW + x;
const uint32_t step = resizeW * resizeH;
if (resizeW < netW && resizeH == netH) {
int dx = (int) (netW - resizeW) / 2;
if (x < dx || x > (resizeW + dx)) {
dst[dR] = .5;
dst[dG] = .5;
dst[dB] = .5;
} else {
dst[dR] = src[y * resizeW + x - dx];
dst[dG] = src[step + y * resizeW + x - dx];
dst[dB] = src[2 * step + y * resizeW + x - dx];
}
} else if (resizeH < netH && resizeW == netW) {
int dy = (int) (netH - resizeH) / 2;
if (y < dy || y > (resizeH + dy)) {
dst[dR] = .5;
dst[dG] = .5;
dst[dB] = .5;
} else {
dst[dR] = src[(y - dy) * resizeW + x];
dst[dG] = src[step + (y - dy) * resizeW + x];
dst[dB] = src[2 * step + (y - dy) * resizeW + x];
}
} else {
dst[dR] = dst[y * resizeW + x];
dst[dG] = dst[step + y * resizeW + x];
dst[dB] = dst[2 * step + y * resizeW + x];
}
}
}测试通过后我将上面4个核函数都处合并成一个,加快效率,最终结果是令人满意的,大概是2ms毫秒就可以处理一张1080P图片,这个没人认真去测,但是总体测试,15路1080P视频包括GPU解码和预处理可以达到实时效果(25fps)